A Comprehensive Guide to Buying Scooter Forks
Prepare yourself for our complete guide to selecting pro scooter forks. We will discuss all the crucial factors you should evaluate before choosing a new freestyle scooter fork. These aspects include compatibility, wheel sizes, wheel offset, and additional considerations.
A perfectly tuned pro scooter requires an exceptional fork. Scooter forks hold your scooter's front wheel in place, and the specifications of your fork determine the wheel sizes you can install—both in terms of width and diameter. Stay follow along to gather some valuable insights on stunt scooter forks!
Overview
Basic Knowledge About Scooter Forks

The fork goes through the headset and the headtube of your deck. The front wheel mounts on the fork, while the compression system, clamps, and bars attach at the top of the fork. Your fork significantly impacts your complete setup as it dictates the wheel sizes you can use on your scooter.
Today, most scooter forks are crafted from a single piece of aluminium, reinforced with various heat treatments. Steel threaded scooter forks were once prevalent but are now outdated due to their reduced durability and increased weight.
Scooter forks compatible with SCS, HIC, and IHC feature a built-in starnut inside the fork tube. The compression bolt fastens into this starnut during the compression system installation.
ICS systems differ as the starnut is housed inside the bar, and the compression bolt is secured through the fork's underside before installing the wheel. Should you have any uncertainties regarding which compression system you have, it's wise to review our in-depth guide:
Considerations like weight, wheel size, wheel offset, and compression play significant roles when selecting a new scooter front fork. This guide covers these topics extensively.
We consistently offer high-quality scooter forks from top brands in the sector, and we likely have one that will meet your needs. Ready to make a decision? We invite you to explore our collection of pro scooter forks:
Understanding Scooter Forks and Wheel Sizes

When opting for a new fork for your scooter, ensure it is compatible with the wheels. Align the wheel size concerning diameter and width. Specifically, the wheel diameter should not surpass the maximum specified for the fork. Also, verify that the width of the wheel hub aligns with or is smaller than the fork’s designated wheel size.
Wheel Diameter
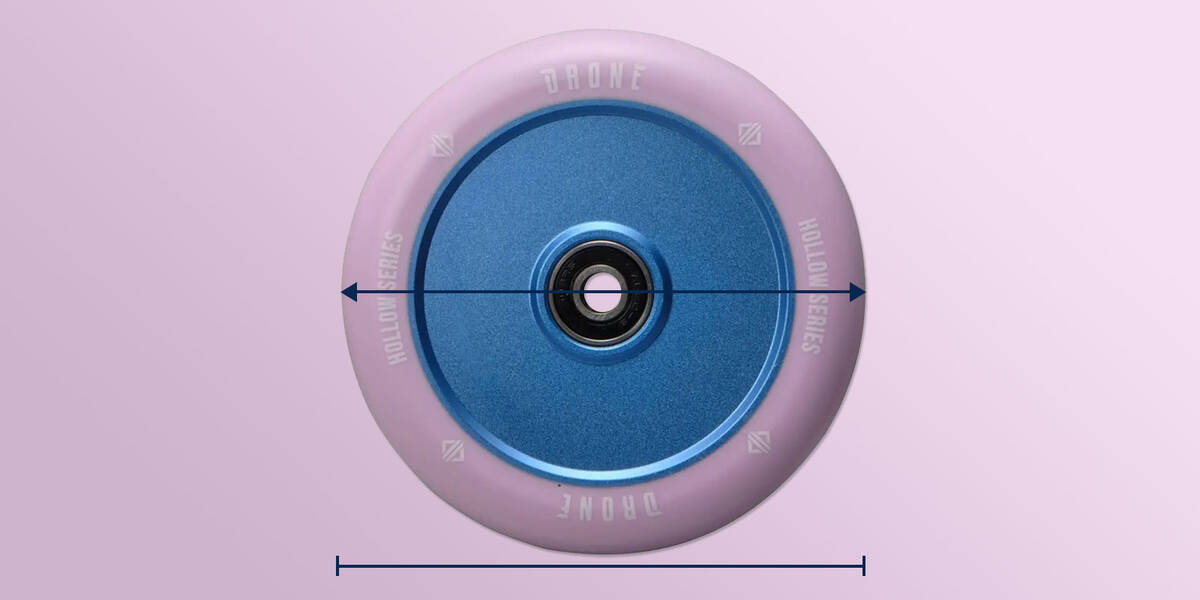
Most scooter forks support wheel diameters of 110 mm, which is the most common size. However, many forks can accommodate wheels up to 125 mm. Just verify that your wheels do not exceed the fork’s capacity, and you’ll be all set.
For instance, if you use wheels with a diameter of 115 mm, you must confirm that your fork can handle wheels of that size or larger.
Wheel Core Width
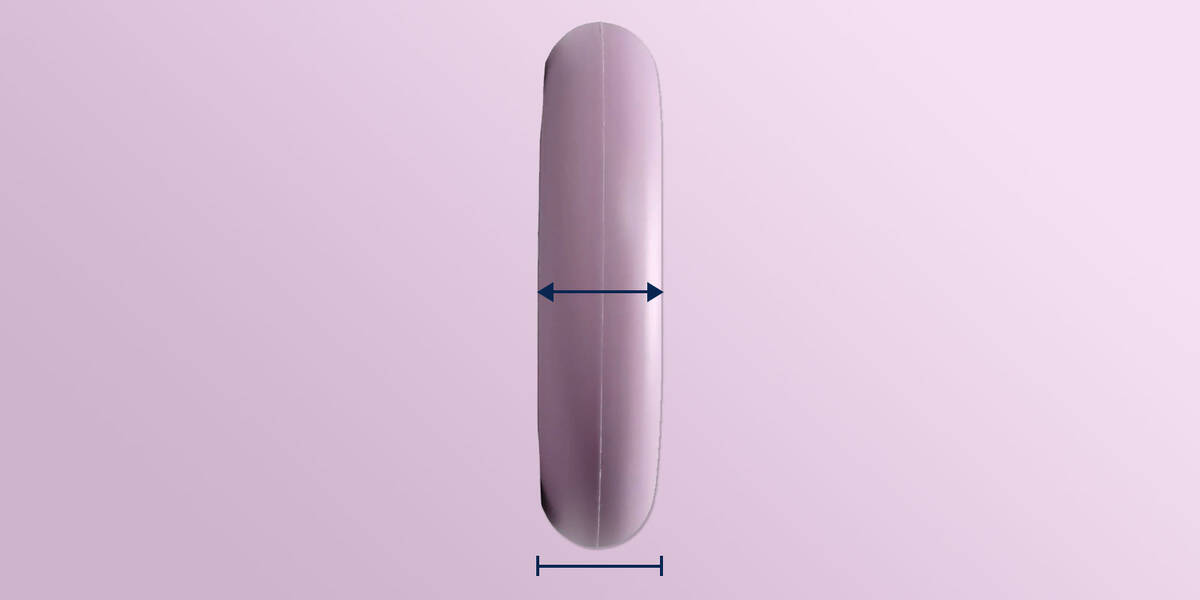
Scooter forks are designed to fit wheels of specific widths, usually between 24 to 30 mm. Within this range, you will find scooter wheels with widths of 26 and 28 mm.
Often, scooter forks include spacers so that a fork that holds 30 mm wide wheels can also fit 24, 26, and 28 mm wheels with the proper spacers.
It’s possible to install wheels narrower than the maximum wheel hub width of a scooter fork, but wheels wider than the fork’s limit (for example, a 30 mm wide wheel for a 24 mm wide fork) won’t fit.
Fork Axle Diameter and Length

The standard wheel axles for scooters have a diameter of 8 mm. However, some forks also support wheel axles with a diameter of 12 mm. Scooters commonly feature 608 bearings, compatible with 8 mm axles. Forks friendly to the 12 standard usually include 8 mm adapters, allowing you to use standard 8 mm axles too.
The appropriate axle length depends on your scooter fork’s width. Ensure the axle is at least as long as the fork’s width, measured externally.
Understanding 12 Standard Scooter Forks
12STD scooter forks are built to accommodate wheel axles with a diameter of 12 mm. A larger axle diameter necessitates bearing size 6001.
A 12-standard pro scooter setup typically features larger and broader wheels. Generally, 12STD pro scooter setups deliver greater speed, stability, and durability at the cost of added weight and reduced agility.
Several 12 standard forks come with spacers enabling them to mount 8 mm axles and regular 608 bearings on the fork.
If transitioning to 12STD, remember that besides the 12STD fork, you’ll need wheels that fit 6001 bearings along with a deck that supports larger wheels and wheel axles. Discover what you need in our selection:
Pro Scooter Forks and Wheel Offset

Wheel offset refers to the distance measured in millimetres from the centre of the fork’s turning axis to the wheel axle. Also known as the rake, wheel offset reveals how far the wheel extends in front of the fork.
The wheel offset significantly impacts the stability and agility of your scooter since it modifies the wheelbase (distance between the front and rear wheels).
A 10 mm wheel offset is the most typical, enhancing stability and control in your overall setup, making steering smoother and more predictable.
Zero-offset forks are highly agile and responsive. Without offset, the front wheel sits closer to the rider, making the scooter more nimble and reactive. Nose manuals are easier with zero-offset forks as your feet are nearer to the ground, simplifying balance. Foot jams are easier too, as more of the wheel engages in the jam.
Scooter Forks & Compression Systems
Forks for SCS and HIC compression are identical. They include a starnut inside the fork tube into which a compression bolt is affixed. The primary difference lies in the compression components around the forks: SCS employs an SCS clamp, whereas HIC utilizes an HIC shim.
IHC compression forks feature a more narrow fork tube, making them ideal for riders who emphasize minimizing overall setup weight. Generally, IHC forks are the lightest scooter forks available.
- SCS Scooter Forks: Standard & oversized bars without slits and oversized or standard-sized SCS clamps
- HIC Scooter Forks: Oversized bars with slits and oversized non-SCS clamps
- IHC Scooter Forks: Standard sized bars and standard sized non-SCS clamps
In ICS and ICS-10 compliant forks, the compression bolt is installed from the fork's base and threads into a starnut lodged inside the bars. Although not commonly found in custom scooters, ICS setups are renowned for being much lighter compared to other compression systems.
If uncertainties arise regarding fork compatibility, these guides could be beneficial:
